Biometrics api
With Android 10, android introduced biometric api. It is important to add security to app, this api makes it easy. All you need to just implement one single api and you can use all the security features which user have in device, like facelock, fingerprint lock, iris. Thanks to google for this awesome api.
Import biometric api
dependencies {
def biometric_version = "1.0.0" //check for latest version
implementation "androidx.biometric:biometric:$biometric_version"
}
Is my device supports biometric authentication?
You can simply check whether device supports biometric API or not with BiometricManager.
val biometricManager = BiometricManager.from(this)
if (biometricManager.canAuthenticate() == BiometricManager.BIOMETRIC_SUCCESS){
Toast.makeText(this, "My device supports biomatric", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
Display biometric prompt
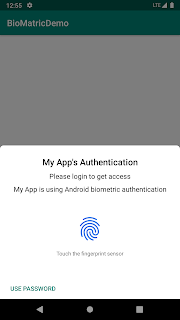
We need instance of BiometricPrompt which requires PromptInfo, display to user. Below methods can be used for that:
private fun instanceOfBiometricPrompt(): BiometricPrompt {
val executor = ContextCompat.getMainExecutor(this)
val callback = object: BiometricPrompt.AuthenticationCallback() {
override fun onAuthenticationError(errorCode: Int, errString: CharSequence) {
super.onAuthenticationError(errorCode, errString)
showMessage("$errorCode :: $errString")
}
override fun onAuthenticationFailed() {
super.onAuthenticationFailed()
showMessage("Authentication failed for an unknown reason")
}
override fun onAuthenticationSucceeded(result: BiometricPrompt.AuthenticationResult) {
super.onAuthenticationSucceeded(result)
showMessage("Authentication was successful")
}
}
return BiometricPrompt(this, executor, callback)
}
private fun getPromptInfo(): BiometricPrompt.PromptInfo {
val promptInfo = BiometricPrompt.PromptInfo.Builder()
.setTitle("My App's Authentication")
.setSubtitle("Please login to get access")
.setDescription("My App is using Android biometric authentication")
.setDeviceCredentialAllowed(true)
.build()
return promptInfo
}
private fun showMessage(s: String) {
Toast.makeText(this, s, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
Note:
This is only used for those devices which have biometric authentication or which supports biometric authentication.
This will use default authentication which used by user for his device.
Pros:
- Single or common UI for all.
- No explicitly check for which authentication way user used
- It also uses its alternative unlock pattern with setDeviceCredentialAllowed(true)